ISRO: Now indigenous atomic clock will decide time on computer-smartphone, dependence on American network will end
ISRO: Atomic clocks are considered to be the most accurate in terms of estimation. These can be calculated in billionths of a second. Every satellite has an atomic clock. It is this atomic clock installed in these satellites located in different orbits that provides positioning information.
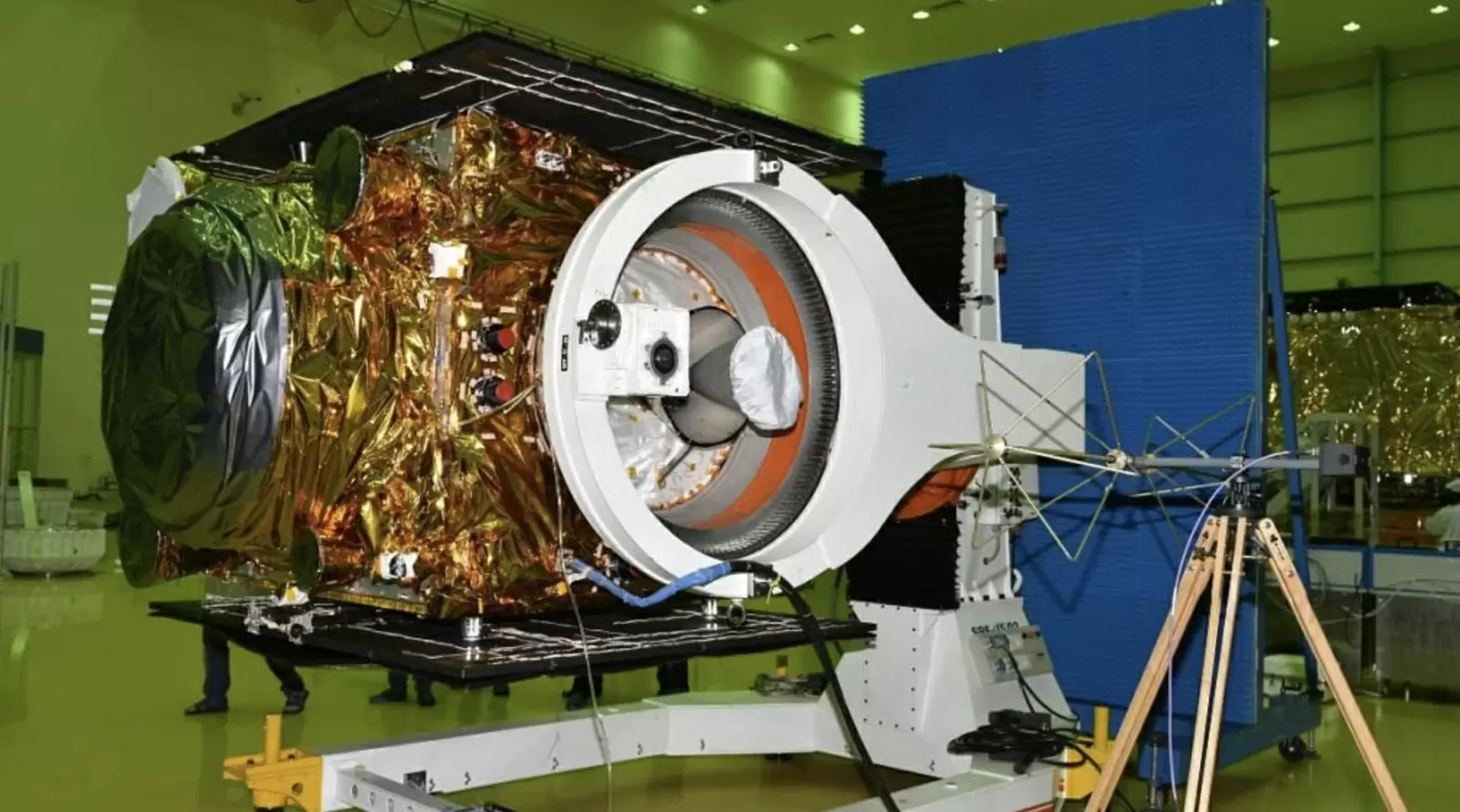

India is all set to integrate home computers and smartphones with the indigenous rubidium atomic clock without any change in its timing. That means this clock will determine the time on our computer and smartphone. With this, India will join the exclusive club of four other countries to do so. Currently, Indian systems on the Internet are connected to the US-based Network Time Protocol. This determines the time on the entire computer network.
This atomic clock has been developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). It was first used in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) or NAVIC. The rubidium atomic clock was created after America denied GPS access to India during the Kargil War. Imported atomic clocks were used in nine NavIC satellites launched between 2013 and 2023. This indigenously developed atomic clock was first used in the 10th and latest version of NAVIC, launched in May 2023.
Estimating clocks that are regarded as the most accurate are atomic clocks. It is possible to compute these in billionths of a second. There is an atomic clock in every satellite. Positioning data is provided by the atomic clock that is installed in these satellites, each of which is in a different orbit. It becomes necessary to launch replacement satellites when the atomic clocks of more than three satellites malfunction.
Want to get your story featured as above? click here!
Want to get your story featured as above? click here!
An alternative to the GPS owned by the US is NAVIGATOR. An alternative to US-owned GPS is NAVIGATOR. Fifteen years ago, the government gave its approval for development. The development cost was 1,420 crore rupees. Due to their accuracy in measuring distance, atomic clocks are also used by navigational satellites.