MIT researchers have developed an inexpensive and long-lasting battery option for electric vehicles
Cobalt-containing batteries are typically used to power electric vehicles. The metal cobalt has significant negative social, environmental, and financial effects. It has been demonstrated by researchers that this material can conduct electricity at rates comparable to cobalt batteries, but at a much lower cost of production than cobalt-containing batteries.
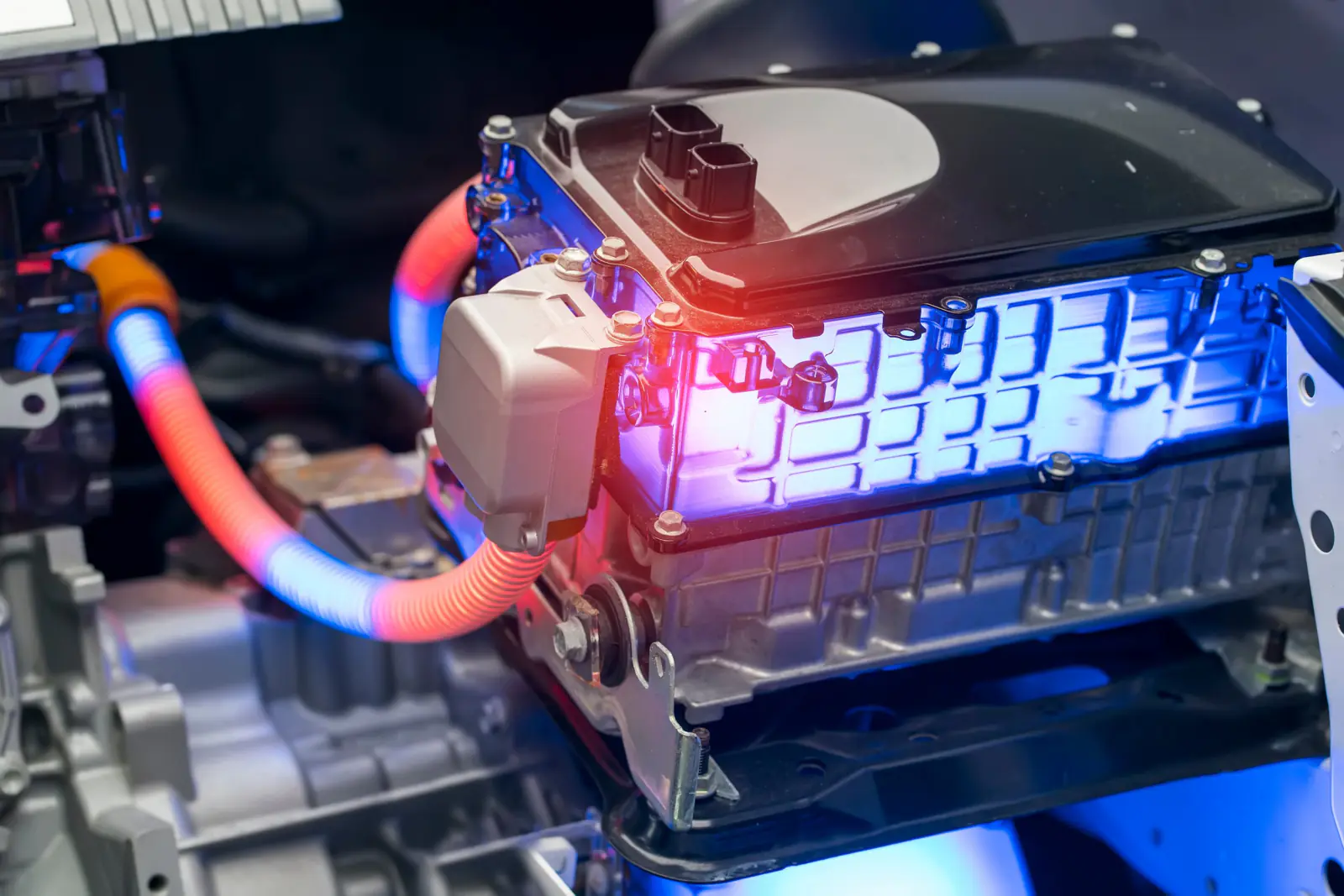
Both domestically and globally, there are always new advancements being made in the field of electric vehicles. In this regard, researchers at MIT have developed a battery material that may provide an environmentally friendly means of supplying electricity for electric vehicles.
Instead of using cobalt or nickel for their cathodes, new lithium-ion batteries use organic materials. Come on, tell us about it.
Cobalt-containing batteries are typically used to power electric vehicles. The metal cobalt has significant negative social, environmental, and financial effects. It has been demonstrated by researchers that this material can conduct electricity at rates comparable to cobalt batteries, but at a much lower cost of production than cobalt-containing batteries.
The researchers say that the novel battery can be charged more quickly and has a comparable storage capacity compared to cobalt batteries. According to tests, this material's conductivity and storage capacity were on par with those of traditional batteries made of cobalt.
Furthermore, TAQ cathode batteries have a higher rate of charge and discharge than conventional batteries, which enables even quicker electron charging rates.
Since cobalt has so many drawbacks, much research has been done to create substitute battery materials. Lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) is a substance that some automakers are beginning to use in their electric vehicles. LFPs, on the other hand, only have half the energy density of nickel and cobalt batteries.







































































