World's first nuclear-powered diamond battery that not need to be charged for thousands
Diamond Battery: Fast-moving electrons emitted during radioactive decay are converted into energy. The synthetic diamond structure captures radiation, just like solar cells convert photons into electricity.
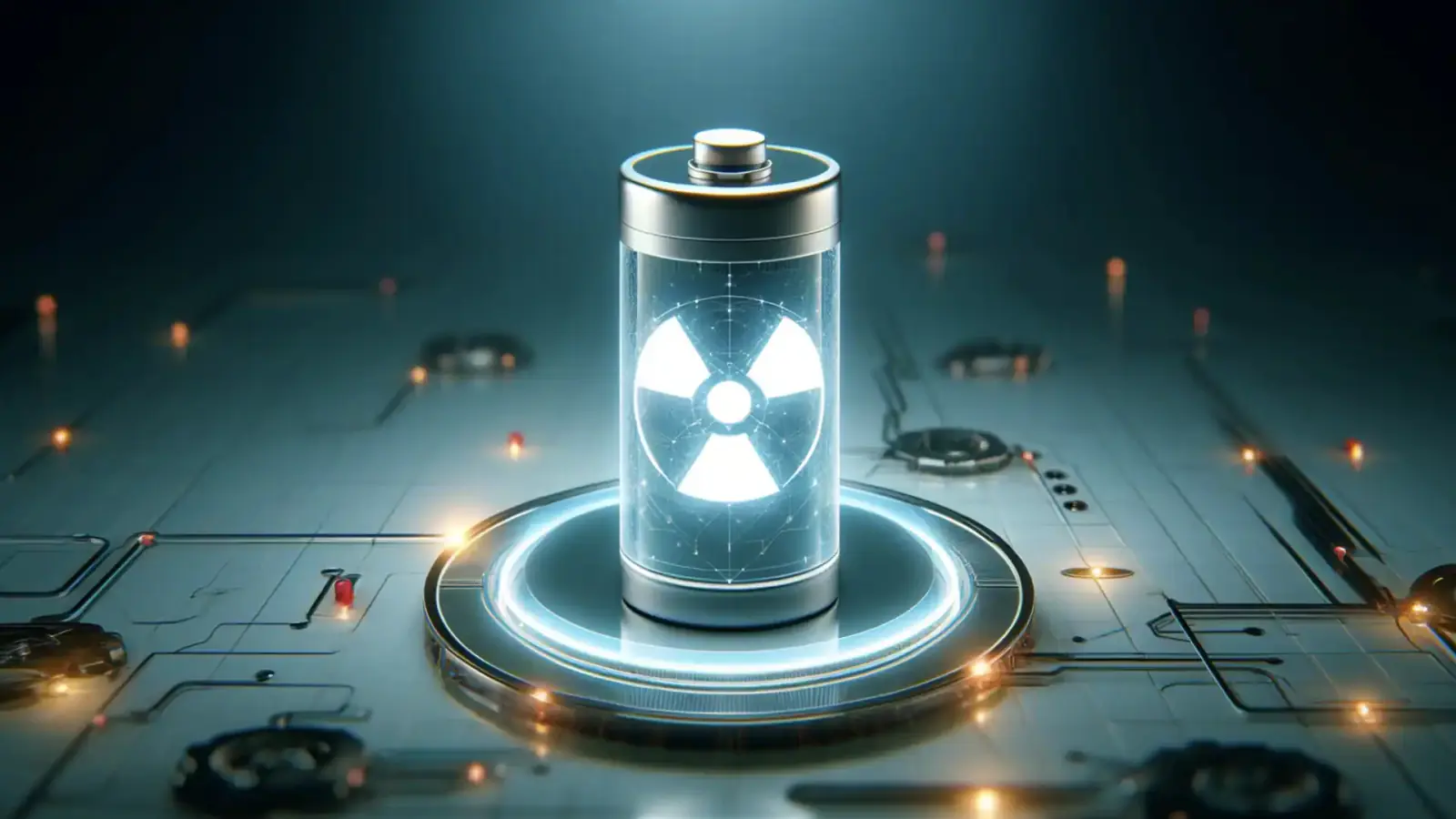

The world's first nuclear power battery that is capable of lasting for thousands of years has been developed by researchers at the University of Bristol, UK. According to reports, this battery uses a radioactive isotope called carbon-14, which has a half-life of 5,730 years. This battery generates electricity by embedding carbon-14 in a diamond-based structure.
Unlike conventional energy sources, this battery does not require any movement or maintenance to produce energy. Fast-moving electrons emitted during radioactive decay are converted into energy. The synthetic diamond structure captures radiation, just like solar cells convert photons into electricity.
Carbon-14 is said to emit low-range radiation, which has been safely enclosed within the diamond casing. That the radiation would not spread around into the environment outside the battery which was safe to use for practical purposes. "Diamond is the hardest material on earth and there is no other material available that offers greater protection, says Professor Neil Fox, energy materials expert at the University of Bristol.
It is said that carbon-14 used in this battery is derived from graphite blocks of nuclear reactors, which it collects on the surface of the isotope. About one gram of carbon-14 buried into a diamond structure yields around 15 joules of energy a day. Though typical AA batteries can provide higher amounts of energy, they deplete rapidly, but these nuclear diamond batteries continue.